 Image source: CenTrio
Image source: CenTrio75%
Energy & Utilities
United States
The energy and utilities sector is crucial to the global energy transition. However, the high costs of modernising and implementing sustainable solutions can be a barrier for asset owners.1 CenTrio, a QIC portfolio company, is addressing this challenge through its district energy operations, offering businesses advanced, efficient energy solutions that enhance operational support and drive sustainable progress.2
Investment background
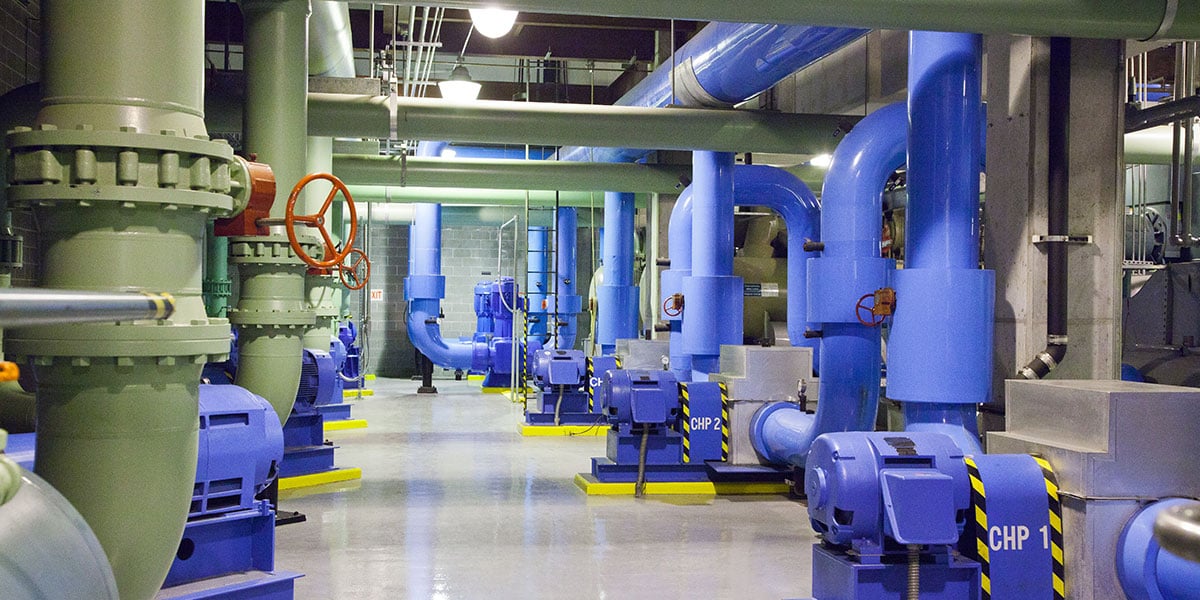
Acquired by QIC in 2021, CenTrio holds one of the largest district energy portfolios in the US, providing cooling, heating and electricity to more than 370 customers, including universities, school districts and hospitals, across 170 million square feet.3 CenTrio’s diverse portfolio of district energy solutions includes notable sustainable systems such as North America’s largest carbon-zero ice battery system located in Chicago4, and also the largest sewer-heat recovery system in Denver5.
CenTrio’s district energy solutions transfer thermal energy in the form of cold water, hot water or steam from a central energy plant to heat and cool buildings, providing a lower-cost, efficient and sustainable alternative for essential in-building heating and cooling.
Beyond traditional energy, CenTrio is increasingly deploying innovative and resilient energy technologies, harnessing the earth’s natural resources as a source of energy and improving the resilience of its energy infrastructure in response to the physical risks posed by climate change.
Active management approach
QIC actively participates on CenTrio’s Board of Directors, guiding the organisation’s strategic direction. Since our acquisition of CenTrio, we have partnered to deliver on several key initiatives, including:
- The carve-out and rebranding of CenTrio (formerly known as Enwave Energy USA), reflecting the centrality of the company’s three core offerings of heating, cooling and electricity, as well as the three benefits of reliability, sustainability and cost-effectiveness for customers.6
- A Sustainable Infrastructure Plan, with short and long-term targets for energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, air pollution, and water consumption, setting the company on a pathway to achieve net zero emissions and decarbonise the entire portfolio by 2050.7
- CenTrio’s inaugural GRESB submission, a key milestone in the company’s sustainability journey. CenTrio received an initial score of 88 in its first year of reporting, compared to the peer average score of 87.8
CenTrio's sustainable district energy solutions
Innovation in action: Operating the largest sewer-heat recovery system in North America9
In 2022, CenTrio partnered with AECOM Technical Services Inc. and Denver-based Saunders Construction to build and operate the National Western Center’s (NWC) sewer-heat recovery system in Denver, the largest sewer-heat recovery system in North America.
Located on a 250-acre master-planned campus less than three miles from downtown Denver, NWC is set to be an innovative urban hub, focusing on entertainment, food, animal health and performance, water, energy, agriculture and sustainability. It will be home to a Colorado State University System campus.
The Denver sewer-heat recovery system utilises a heat pump to capture wastewater heat and transfers it to a clean water distribution pipe that enters individual buildings. This closed-loop system ensures that wastewater does not come in contact with the clean water. The wastewater then returns to the sewer, while the heat is distributed to the clean water to efficiently heat and cool the buildings.
CenTrio Denver: Heating and cooling using a recycled source of thermal energy - wastewater
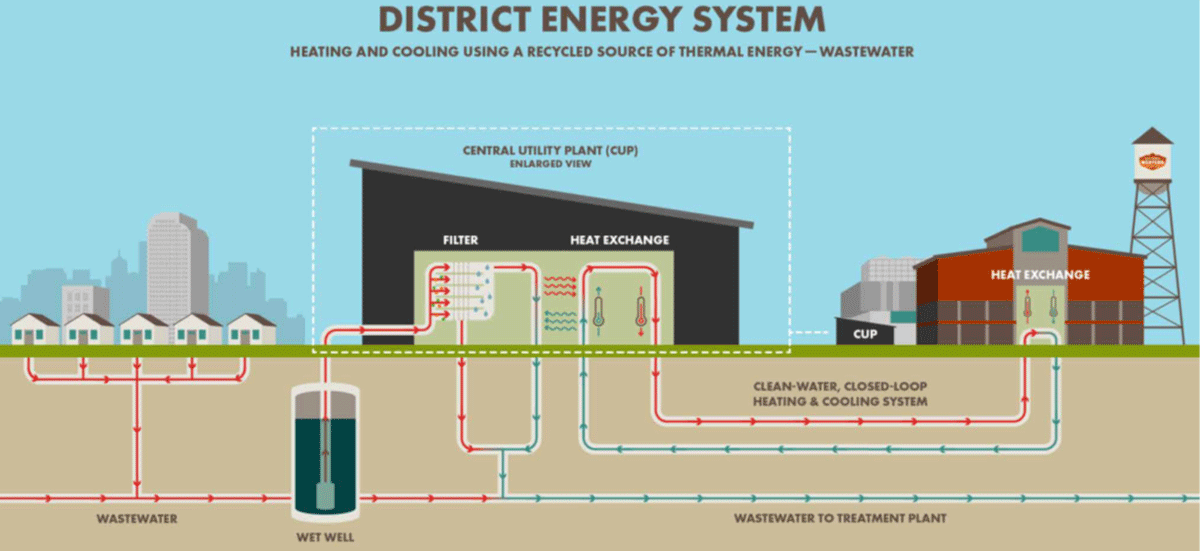 CenTrio Denver: Heating and cooling using a recycled source of thermal energy - wastewater
CenTrio Denver: Heating and cooling using a recycled source of thermal energy - wastewater
The NWC campus sources nearly 90% of its heating and cooling from the sewer-heat system, avoiding the burning of fossil fuels, as well as:
- Eliminates approximately 2,600 metric tonnes of CO2 each year – the emissions equivalent of driving a car 10.6 million kilometres
- Conserves the equivalent of five Olympic swimming pools worth of water each year.
Resilience in action: Future-proofing energy supply for essential services
CenTrio operates a district energy facility in New Orleans that provides both chilled water and steam to 24 buildings including key higher education and healthcare institutions, such as the Health Sciences Center, University Medical Center and Louisiana Cancer Research Center.10
Given the critical nature of these services, reliability is paramount, and climate resilience has been a key focus in the design and operation of the facility:
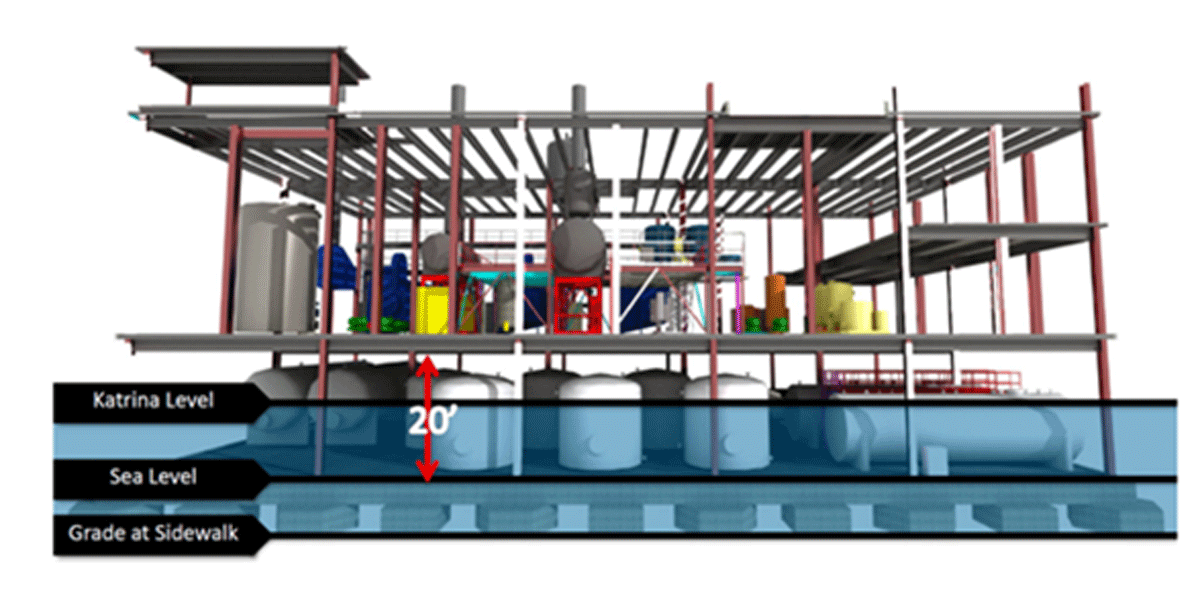
- Elevated Design: In response to rising sea levels11, the building is raised five feet above sea level, with all critical systems installed at least 20 feet above sea level.
- Wind Resistance: The facility is engineered to endure wind speeds of up to 150 miles per hour, addressing the city’s vulnerability to hurricanes.
- Emergency Preparedness: Backup generation capabilities are integrated into the facility, and staff undergo rigorous emergency response training.
These design features and systems were tested by Hurricane Katrina, which the facility withstood, continuously delivering essential services to the healthcare institutions and wider community throughout the extreme weather event.
References
- International Energy Agency, 2021. The cost of capital in clean energy transitions. https://www.iea.org/articles/the-cost-of-capital-in-clean-energy-transitions.
- There is no guarantee that any of the steps taken by QIC and/or third parties to mitigate, prevent or otherwise address material ESG topics will be successful, completed as expected or at all, or will apply to or continue to be implemented in the future.
- Source: CenTrio.
- CenTrio. Our districts – Chicago. https://www.centrioenergy.com/our-districts/chicago/.
- CenTrio. Our districts – Denver. https://www.centrioenergy.com/our-districts/denver/.
- Centrio, 2021. Enwave’s US district energy business announces new name, CenTrio. https://www.centrioenergy.com/news/enwave-s-u-s-district-energy-business-announces-new-name-centrio/.
- The QIC Board has resolved to embark on a pathway to achieve net zero carbon emissions by 2050 or sooner. To this end, QIC has become a signatory to the Net Zero Asset Managers (NZAM) Initiative. NZAM is a leading net zero coalition in the finance sector, committed to supporting the goal of net zero carbon emissions by 2050 or sooner.
- QIC is an investor member of GRESB and pays an annual fee.
- QIC Infrastructure Sustainability Report 2023.
- Centrio. Our districts – New Orleans. https://www.centrioenergy.com/our-districts/new-orleans/.
- City of New Orleans. Net zero by 2050: A priority list for climate action in New Orleans. https://nola.gov/climate-action/.
Further information
This document is subject to the QIC Disclaimer and website access terms and conditions.
ESG
Certain information contained herein relating to ESG goals, targets, intentions, or expectations, including with respect to net zero targets and related timelines, is subject to change, and no assurance can be given that such goals, targets, intentions, or expectations will be met. ESG-related calculation methodologies and data collection practices and the reporting thereof as a whole are evolving, and other asset managers are implementing different frameworks, methodologies, and tracking tools. The selection of such different but acceptable measurement techniques can result in materially different measurements. Further, these techniques are subject to measurement uncertainties resulting from inherent limitations in the nature and methods used to determine such data. The precision of different measurement techniques may also vary.
Infrastructure Net Zero Emissions Targets
QIC Infrastructure’s net zero target also includes a 50% reduction in scope 1 & 2 emissions by 2030 from a 2020 baseline, which applies to the equity share of emissions for assets in the QIC Infrastructure Portfolio (QIP) and QIC Global Infrastructure Fund I (QGIF I). For infrastructure assets, the net zero pathway incorporates four pillars: operational and design efficiencies; transition to low-carbon fuels and renewable electricity; leveraging emerging technologies; and if required, management of residual emissions through purchase of verified, efficient, measurable carbon offsets.
Asset Summaries
The asset transaction summaries presented or referred to herein may not be representative of all transactions of a given type or of investments generally and are described for informational and illustrative purposes only. The information contained herein references and describes specific investment opportunities that QIC has previously pursued, and it should not be assumed that these investments, or any future investments made by QIC, will ultimately be profitable. The information provided should not be deemed a recommendation to invest in the investments mentioned. Recipients should also note that the asset transaction summaries presented or referred to herein have involved QIC professionals who may be involved with the management and operations of the investment as well as other QIC personnel who will not be involved in the management and operations of the investment. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future performance.
